China is ramping up its efforts to explore the universe as it is set to launch its space telescope ‘Xuntian’ next year. Known as China’s own ‘Hubble,’ authorities in Beijing claim it outmatches the NASA and European Space Agency (ESA) telescope’s capabilities.
The flagship telescope is intended to reveal new insights into faraway galaxies, mysterious dark matter, dark energy, and the universe’s past and future evolution, Chinese news agency Xinhua reported.
A space telescope, also known as a space observatory, is a telescope that is used to observe celestial objects from outer space.
The Chinese Survey Space Telescope (CSST) or the Xuntian Space Telescope is a space-based optical observatory that will allow astronomers to conduct sky surveys and capture a general map or photographs of the sky.
The Xuntian will photograph 40% of the sky and relay vast data to Earth for examination by scientists all over the world, according to Li Ran, project scientist of the CSST Scientific Data Reduction System. Its major goal is to address the universe’s most fundamental problems.

Chinese researchers have stated that the telescope will measure the positions, shapes, and brightness of nearly one billion galaxies, which could help explain how they evolve.
It will also aid in determining the upper limit of neutrino mass and shed light on the enigmatic dark matter and dark energy that make up the vast majority of the universe’s mass-energy content.
The Xuntian telescope will be connected to the Space Station Tiangong, which will become operational later this year. It was originally intended to be put on Tiangong, but there were concerns about vibration, contamination, stray light, and line-of-sight obstruction from the space station.
Later, a radical design was adopted, and it was decided that the telescope would be placed in the same orbit as the space station but kept far apart during normal operations and docked with the space station only when necessary.

“The telescope can bring China’s research in optical astronomy to the forefront and help cultivate world-class Chinese scientists. It can also take breathtaking pictures, allowing the public to understand the universe directly,” Li added.
Yet to be launched, this telescope is widely compared to the Hubble, which was developed jointly by NASA and ESA. The Hubble was the first-ever ‘sophisticated’ space telescope, leading to numerous important discoveries and observations.
The CSST will allow China to undertake advanced space exploration activities, which are imperative to achieve its goal of global space dominance.
Is Xuntian A Challenger To Hubble?
The Xuntian is a bus-sized facility with the height of a three-story building. In an exclusive interview with Xinhua, Liu Jifeng, deputy director of the National Astronomical Observatories of China (NAOC), claimed that while the telescope’s aperture is two meters, it has a field of view 350 times larger than that of Hubble.
According to Chinese researchers, the CSST has a three-mirror anastigmat design (no optical aberrations) that enables it to attain exceptional image quality within a large field of vision. It’s an off-axis Cook telescope with no obstructions that, when correctly sampled, may reach higher precision in photometry, location, and form measurements.
Five types of equipment, including a survey camera, will be mounted on the CSST. According to researchers, the camera’s main focal plane is equipped with thirty 81-megapixel detectors that will capture images and spectra of around 17,500 square degrees of the median-to-high galactic and median-to-high ecliptic latitude sky in different bands.
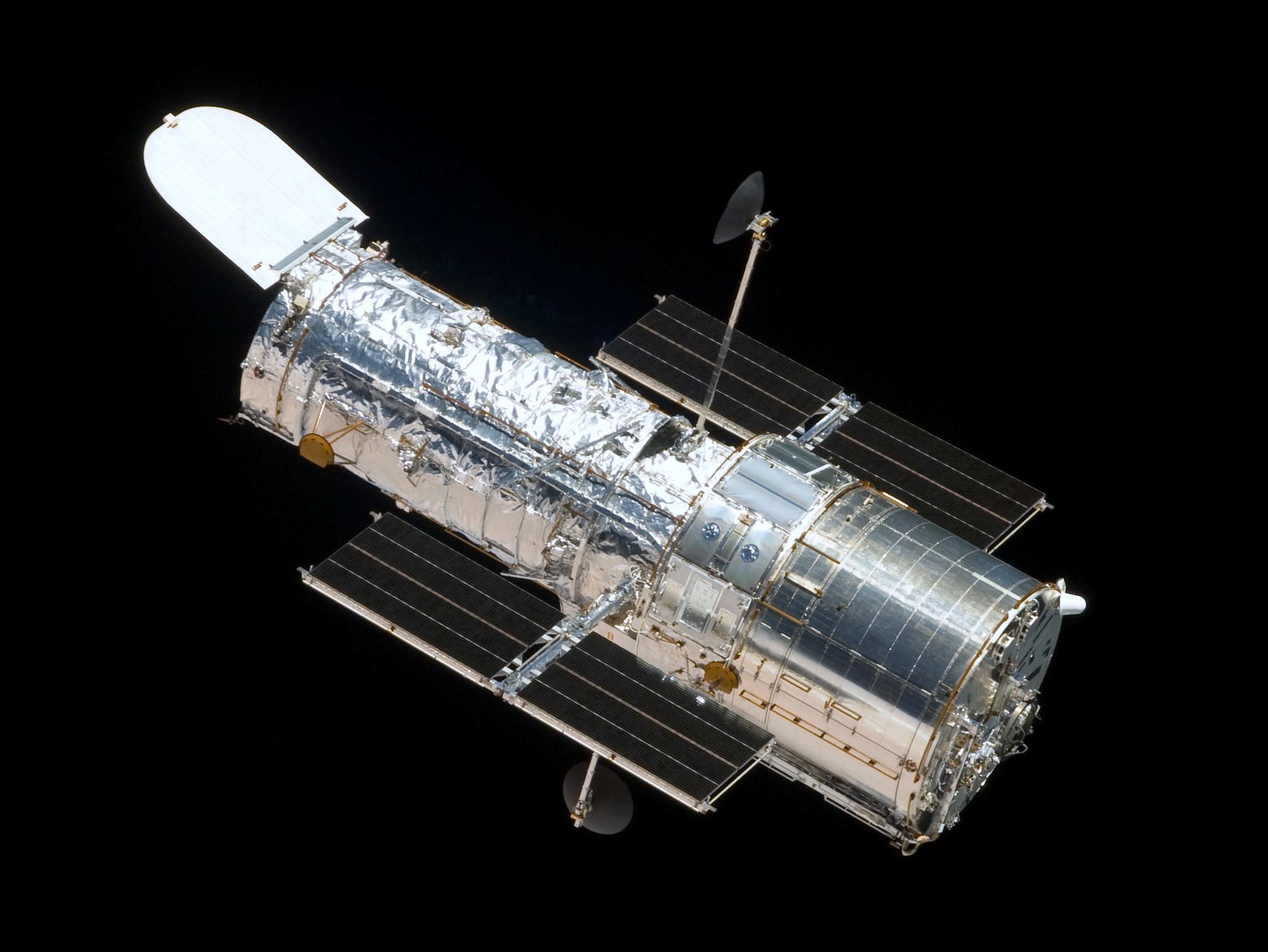

On the other hand, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) has a 2.4-meter (94-inch) primary mirror, a smaller secondary mirror, and several recording devices that can detect visibly, ultraviolet, and infrared light.
The most important of its equipment, the wide-field planetary camera, can acquire wide-field or high-resolution photographs of planets and galactic and extragalactic objects.
The findings made by the HST are believed to have transformed astronomy. The first exact measurement of Hubble’s constant, which is the rate of the universe’s expansion, came from its observations of Cepheid variables in nearby galaxies.
The HST has also photographed young stars with discs that will someday become planetary systems.
An image of around 1,500 galaxies called the Hubble Deep Field reveals galactic evolution throughout nearly the entire history of the cosmos. The HST was also used to discover Hydra and Nix, two moons of the dwarf planet Pluto, making it an exceptional space telescope within the solar system.
Prototype of Xuntian Space Telescope (photo taken in 2021). The telescope is planned to launch in 2023 and fly with China Space Station in the same orbit#CSST #Tiangong pic.twitter.com/PwqW2waEwW
— China Spaceflight ? (@CNSpaceflight) April 2, 2022
However, the Project Scientist of the CSST Optical Facility Zhan Hu claims that the CSST will most likely be the largest space telescope for astronomy in the near-ultraviolet visible category in the decade before 2035. The CSST can dock with the space station as needed for refueling and servicing, making its maintenance less expensive than Hubble.
From 1993 to 2009, NASA performed five space shuttle servicing missions to perform repairs, replace parts, and install new equipment for Hubble.
Further, the CSST is scheduled to begin scientific operations in 2024 and has a 10-year mission lifespan that could be extended in theory.
Having said that, while it is true that the HST has attained an advanced age, it also has a successor that is set to take forward the distinguished legacy established by HST. The Hubble will eventually be succeeded by the James Webb telescope, which was launched in 2021.
Intrigued by the claims of Chinese researchers about the CSST or Xuntian, EurAsian Times spoke to a space expert to know if it holds water. Space and Defense Analyst Girish Linganna told the EurAsian Times: “When it comes to reflecting telescopes, the key component is the size of its curved mirror.
You could sort of think of a telescope mirror like a light bucket, the more light you can collect in this bucket, the fainter and farther-away things you can see in the universe. Hubble’s mirror was an impressive 7.8 feet ( 2.37 meters) in diameter.
Hubble Space Telescope is living on borrowed time. The iconic satellite was only supposed to be in operation for 15 years and has now lasted for more than 30. For the last three decades, Hubble has been the biggest and most powerful space telescope ever built.
The main mirror in Xuntian will have a diameter of around two meters (six-and-a-half feet) across, roughly the size of the mirror at the heart of the Hubble Space Telescope. Slightly smaller than Hubble, Xuntian will not quite match its predecessor’s resolution as many agencies do claim.”
These observations would not convince China as it believes that Xuntian will outmatch the Hubble in terms of exploration. Not just that, it aims to take on the missions that Hubble has been undertaking. For example, China wants to observe and record the movement of Uranus, which Hubble has made several observations of.
For China, which aspires to challenge the hegemony of the US Space program, a space telescope of this caliber could be of great importance even if it does not outmatch the capability of the Hubble or, the James Webb.
Having said that, more will become known about the Xuntian once it is launched and its mission kick-started.
- Contact the author at sakshi.tiwari9555@gmail.com
- Follow EurAsian Times on Google News




